When it comes to spinal health, understanding the subtle yet critical differences in disc pathology can significantly affect treatment outcomes and patient quality of life. Disc extrusion and sequestration are two forms of spinal disc herniation that, while related, present distinct characteristics on MRI scans and necessitate different clinical approaches. In 2025, the integration of advanced imaging technologies from leading manufacturers such as Siemens Healthineers, GE Healthcare, Philips, and Canon Medical Systems enhances the precision of diagnosis, allowing experts like Dr. Sylvain Desforges to tailor personalized treatments effectively. This article delves deeply into the MRI findings that differentiate disc extrusion from sequestration, exploring the anatomical, clinical, and therapeutic implications of each condition to assist patients and healthcare providers in making informed decisions.
The spine’s intricate anatomy, combined with the complexity of disc pathologies, requires a comprehensive understanding that goes beyond textbook definitions. For instance, a disc extrusion involves the nucleus pulposus breaking through the annulus fibrosus but remaining connected to the disc, whereas sequestration is characterized by a free fragment completely detached and displaced within the spinal canal. These nuances influence symptom presentation, diagnostic challenges, and treatment planning. Technologies from companies such as Hitachi Medical Systems and Esaote contribute high-resolution imaging that detects subtle tissue changes, while strategies involving Medtronic and Stryker devices provide innovative treatment options in modern clinics.
Understanding the Anatomy and Pathophysiology of Disc Extrusion and Sequestration
Disc herniations represent a spectrum of conditions resulting from the displacement of nucleus pulposus material beyond the intervertebral disc space. The two significant types—disc extrusion and sequestration—differ mainly in the relationship of the displaced material to the parent disc. In disc extrusion, the inner gel-like nucleus pulposus punctures the tough outer annulus fibrosus but remains partially attached with a narrow stalk. This results in a defined protrusion into the spinal canal that may compress nerves.
In contrast, sequestration occurs when a fragment of the disc completely separates from the main disc body, forming a free fragment that may migrate along the epidural space. This free fragment can cause significant inflammation and nerve irritation due to its mobility and direct contact with neural elements. The pathophysiological consequences influence symptoms and treatment responses.
Key Differences in MRI Appearance
- Disc Extrusion: MRI reveals a displaced disc material extending beyond the confines of the intervertebral disc space with a narrow base of attachment. The extruded material may maintain continuity with the parent disc on sagittal and axial views.
- Sequestration (Sequestered Disc): Imaging shows a fragment completely separated from the disc’s remaining material, often appearing as an isolated hypointense or isointense mass in T1- and T2-weighted MRI images, usually located in the anterior epidural space.
Advanced imaging equipment by Fujifilm Healthcare and Siemens Healthineers equipped with high field-strength magnets improves visualization of these pathologies, enabling more accurate differentiation. This clarity guides the clinical team in avoiding unnecessary invasive procedures when conservative management is viable.
| Feature | Disc Extrusion | Sequestration |
|---|---|---|
| Continuity with Parent Disc | Maintained | Lost (Free Fragment) |
| Base Width of Disc Material | Narrow Neck | Not Applicable |
| Location of Disc Material | Extending into Spinal Canal | Displaced into Epidural Space |
| Potential for Migration | Limited | High (Fragment Can Migrate) |
| Clinical Severity | Moderate to Severe | Severe |
Emerging MRI techniques like 3D SPACE sequences and diffusion tensor imaging, available through partnerships with GE Healthcare and Philips, offer enhanced delineation of the disc fragments and their relationship with nerves and surrounding tissues. Such innovations underpin Dr. Desforges’ commitment to scientific rigor and ethical practice, ensuring that patients receive a thoroughly evaluated and transparent diagnosis.
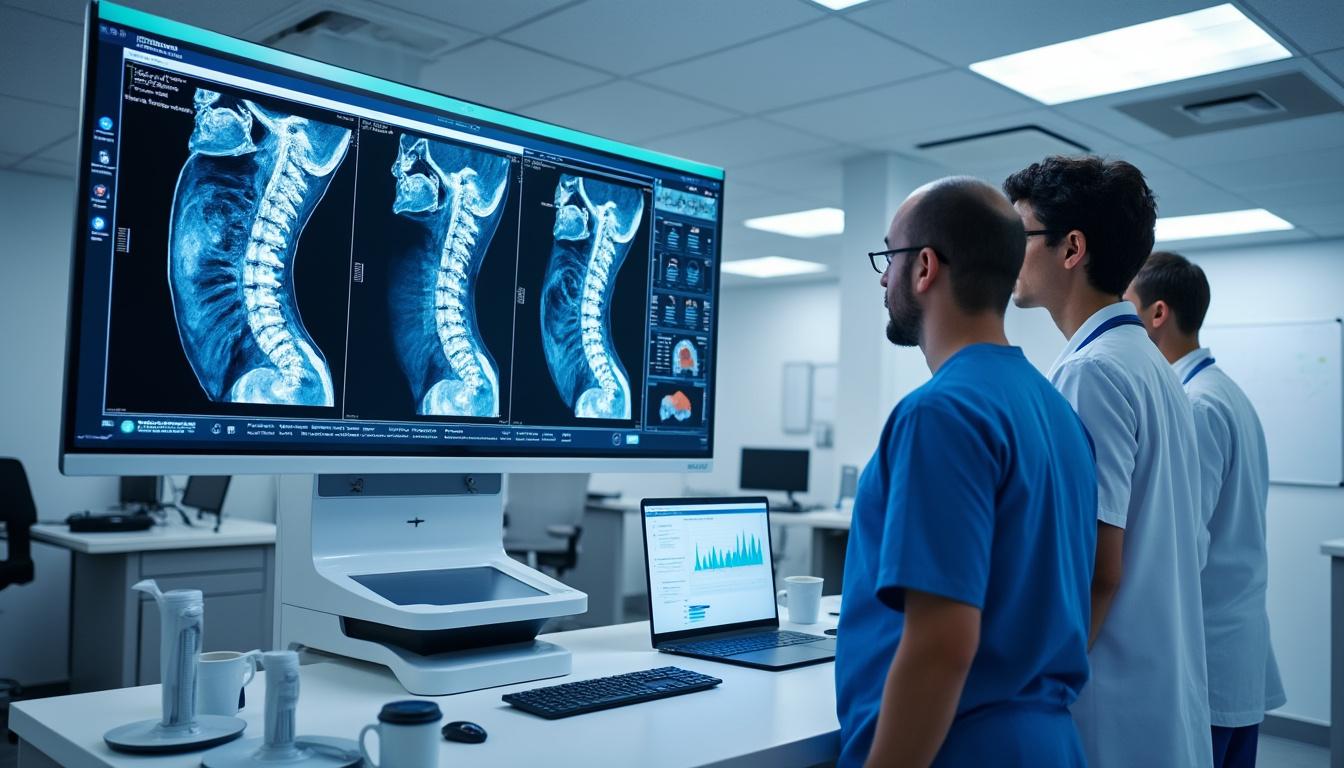
Clinical Presentation: Symptoms Associated with Disc Extrusion vs Sequestration
The clinical symptoms accompanying disc extrusion and sequestration can overlap but typically vary in intensity and neurological impact. Patients with a disc extrusion often experience localized pain that may radiate depending on nerve root involvement. Symptoms include:
- Sharp or burning localized back or neck pain
- Radiculopathy causing pain radiating to limbs
- Numbness or tingling in the affected dermatome
- Muscle weakness related to nerve compression
Meanwhile, sequestrated discs usually present more severe symptoms due to free fragment mobility and nerve root or dural sac irritation. This may include:
- Severe radicular pain often resistant to conservative treatment
- Neurological deficits such as muscle atrophy or loss of reflexes
- Possible cauda equina syndrome in rare cases due to fragment migration near the lower spinal canal
Dr. Sylvain Desforges emphasizes personalized patient evaluation to identify symptom patterns aligned with imaging findings. His extensive experience allows distinguishing symptoms that mandate urgent care, employing multidisciplinary approaches integrating osteopathic manipulation, physical therapy, and when appropriate, referrals for advanced interventions with innovators such as Medtronic and Zimmer Biomet technologies.
| Symptom | Disc Extrusion | Sequestration |
|---|---|---|
| Pain Severity | Moderate to Severe | Severe |
| Neurological Deficits | Possible | Common |
| Nerve Root Compression | Frequent | Frequent and More Extensive |
| Response to Conservative Treatment | Often Effective | Sometimes Requires Intervention |
Early recognition and differentiation support timely intervention, decreasing the risk of chronic disability and optimizing patient outcomes. Collaborations with Philips and Hitachi Medical Systems improve imaging workflows and patient comfort during diagnostics, reflecting Dr. Desforges’ holistic, patient-centered philosophy.
MRI Protocols and Imaging Techniques Specific to Disc Extrusion and Sequestration
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) remains the gold standard for evaluating spinal disc pathology. The primary advantage lies in its ability to clearly image soft tissues, differentiating between annulus fibrosus, nucleus pulposus, nerve roots, and surrounding ligaments. Advanced MRI sequences enhance diagnostic accuracy in discriminating extrusion from sequestration:
- T1-Weighted Imaging (T1WI): Provides excellent anatomical detail, highlighting marrow and disc material signal intensity differences.
- T2-Weighted Imaging (T2WI): Ideal for detecting disc hydration status; extruded or sequestered fragments often show decreased T2 signal due to dehydration.
- 3D SPACE MRI: Developed by Siemens Healthineers, offers isotropic resolution allowing multiplanar reconstruction, improving the visualization of free fragments in sequestration.
- Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI): Emerging method to assess nerve root integrity and potential compression severity, aiding in treatment planning.
- Fat-Suppressed Sequences: Help differentiate inflammatory changes associated with sequestrated fragments.
Among the leading MRI equipment providers in Québec and globally, companies like Canon Medical Systems and Esaote facilitate integration of these sequences within clinical workflows. This leads to shorter scan times and less patient discomfort, crucial for patients with acute back pain.
| Imaging Technique | Purpose | Contribution to Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|
| T1 Weighted | Anatomical detail and disc appearance | Highlights disc boundaries and marrow fat content |
| T2 Weighted | Hydration state of disc material | Identifies desiccation and extrusion extent |
| 3D SPACE MRI | High-resolution multiplanar imaging | Detects fragment displacement and nerve relation |
| DTI | Nerve integrity | Evaluates nerve root involvement for prognosis |
| Fat-Suppression | Inflammation visualization | Differentiates sequestered fragments with inflammation |
Equipped with the latest MRI technology, institutions like Cliniques TAGMED led by Dr. Desforges pioneer diagnostic accuracy while maintaining patient comfort and adherence to regulatory standards established by Quebec and Canadian health authorities.
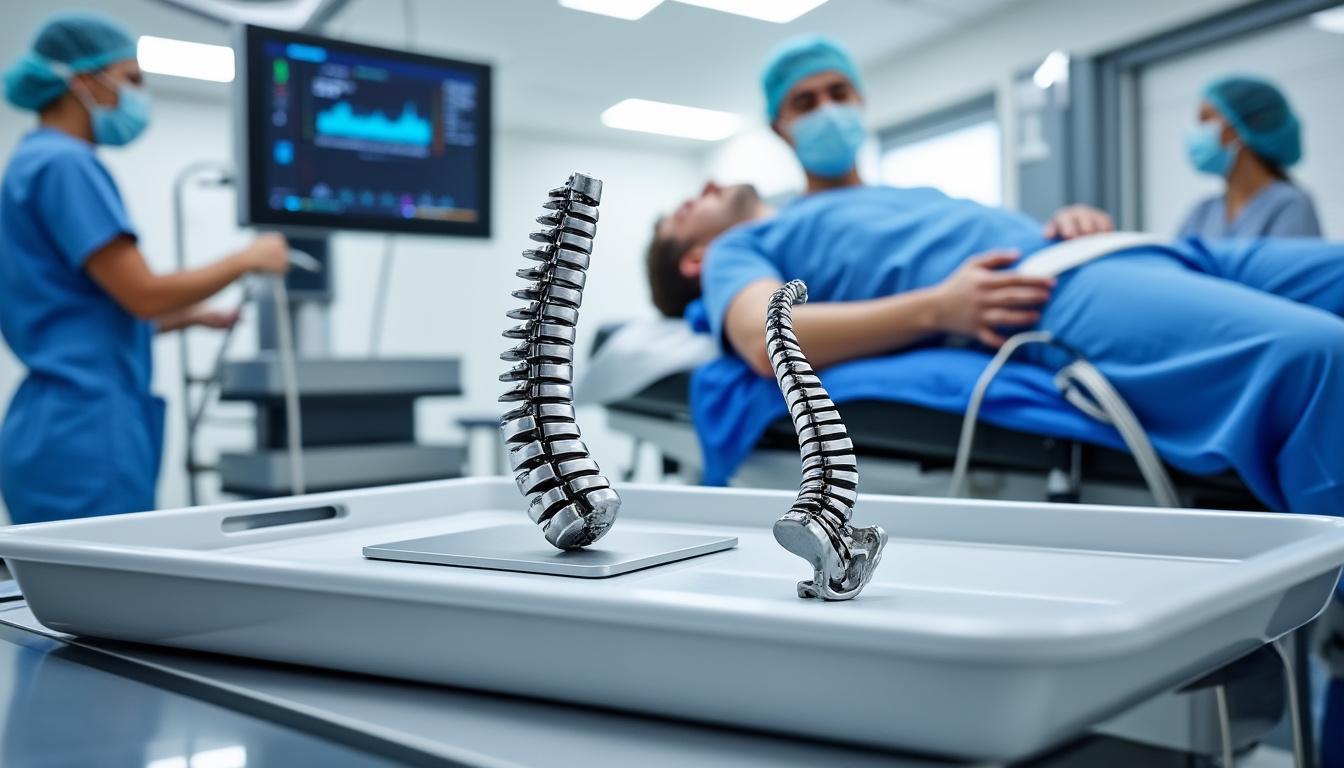
Managing Disc Extrusion and Sequestration: Evidence-Based Treatment Pathways
Treatment for disc extrusion and sequestration demands a nuanced approach that balances efficacy with safety, always respecting ethical standards and patient preferences. Comprehensive evaluation is the cornerstone before tailoring a strategy that may range from conservative care to minimally invasive procedures.
Typical management options include:
- Conservative Therapy: Physical therapy focusing on spinal stabilization, postural correction, and pain management through modalities like laser therapy.
- Pharmacologic Treatments: NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, and short courses of oral corticosteroids administered carefully under medical supervision.
- Injections: Image-guided epidural steroid injections or nerve blocks designed to reduce inflammation and alleviate radicular pain.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Techniques such as endoscopic discectomy, spinal decompression devices by Medtronic, and biologic treatments including platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and the Discseel procedure.
- Surgical Intervention: Reserved for refractory cases or those presenting neurological deficits, performed with equipment from Stryker and Zimmer Biomet ensuring precision and safety.
Dr. Sylvain Desforges’ clinical expertise promotes a personalized approach emphasizing non-surgical interventions first, based on robust scientific evidence and patient-centered values. His affiliations with renowned institutions and professional bodies underscore his commitment to continuous innovation and ethical practice.
| Treatment Option | Indications | Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Mild to moderate symptoms | Improves function, reduces pain | Low risk |
| Medications | Inflammation, pain control | Symptomatic relief | Gastrointestinal, systemic side effects |
| Epidural Injections | Persistent radiculopathy | Targeted pain relief | Infection, bleeding |
| Minimally Invasive Procedures | Unresponsive to conservative care | Reduced recovery time | Procedure-related complications |
| Surgery | Neurological deficits or failed non-surgical treatment | Definitive decompression | Surgical risks, recovery time |
The Role of Advanced Technologies in Diagnosis and Treatment
The rapid advancement of medical technology profoundly impacts the management of disc extrusion and sequestration. MRI scanners from industry leaders like GE Healthcare and Hitachi Medical Systems now deliver ultra-high resolution images that reveal disc morphology with unmatched clarity. Such technological breakthroughs enable clinicians like Dr. Desforges to push the boundaries in patient assessment and precision medicine.
On the treatment front, dynamic spinal implants from Zimmer Biomet and minimally invasive instrumentation by Stryker revolutionize surgical options, affording faster healing and better functional outcomes. Non-surgical innovations including laser therapy and neurovertebral decompression devices provide alternatives for patients hesitant about surgery.
Dr. Desforges integrates these tools within a framework of scientific rigor, ensuring that every intervention aligns with prevailing guidelines from the Collège des médecins du Québec and Canadian medical authorities. This adherence guarantees patient safety while fostering innovation.
| Technology | Manufacturer | Application | Clinical Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRI Scanner | Siemens Healthineers, GE Healthcare, Philips | Imaging and diagnosis | Precise herniation classification |
| Dynamic Spinal Implants | Zimmer Biomet | Surgical stabilization | Enhanced spinal mobility post-op |
| Neurovertebral Decompression Device | Medtronic | Non-surgical spinal decompression | Pain relief, nerve decompression |
| Laser Therapy Equipment | Hitachi Medical Systems, Fujifilm Healthcare | Minimally invasive treatment | Reduces inflammation, accelerates healing |
Patient Education and the Importance of Personalized Care
Clear communication and education empower patients to actively participate in managing their spinal health. Dr. Sylvain Desforges prioritizes accessible explanations of complex medical concepts, making diagnosis and treatment understandable without overwhelming medical jargon. Each patient’s case receives a thorough evaluation, considering personal history, lifestyle, and specific imaging results.
- Explaining MRI findings in simple terms to reduce anxiety
- Discussing conservative versus surgical options transparently
- Setting realistic expectations about treatment outcomes
- Encouraging questions to foster a collaborative care environment
This empathetic approach respects each individual’s unique situation, assuring that therapeutic choices align with patient values and goals. The emphasis on continuing education and innovation encourages patients to consider advanced options like minimally invasive procedures or emerging biologic therapies when appropriate.
| Patient Education Element | Purpose | Impact on Care |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Language Explanation | Improve understanding | Reduce anxiety and improve compliance |
| Transparent Discussion of Options | Empower decision-making | Patient-centered treatment plans |
| Expectation Management | Set realistic goals | Increased satisfaction and outcomes |
| Open Communication | Build trust | Enhanced therapeutic alliance |
The Significance of Early Diagnosis and Follow-up in Spinal Disc Disorders
Early and accurate differentiation between disc extrusion and sequestration is vital for successful management. Delay in diagnosis can escalate symptoms and worsen prognosis, leading to chronic pain and disability. State-of-the-art imaging combined with clinical expertise allows for timely intervention to prevent irreversible nerve damage.
Consistent follow-up is equally important. It ensures treatment efficacy, monitors for complications, and adjusts care plans responsive to patient progress. Dr. Desforges advocates scheduled reassessments supported by repeat imaging if symptoms evolve or fail to improve, a practice aligned with current Canadian and Quebec medical guidelines.
- Routine clinical evaluations post-treatment
- Imaging follow-up when clinically indicated
- Functional assessments to guide rehabilitation
- Patient-reported outcomes to tailor ongoing care
This vigilant surveillance model exemplifies the commitment to patient safety and optimized outcomes cultivated at Cliniques TAGMED and through the Canadian College of Osteopaths under Dr. Desforges’ leadership.
| Follow-up Activity | Purpose | Recommended Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Evaluation | Monitor symptom progression | Every 4-6 weeks initially |
| Repeat MRI | Assess healing or fragment migration | As symptoms dictate |
| Rehabilitation Assessment | Adapt therapy plans | Monthly or as needed |
| Patient Feedback | Individualized care adjustments | Ongoing |
Collaborative Spine Care Networks and Their Role in Patient Outcomes
The complexity of disc extrusions and sequestrations often requires a multidisciplinary approach involving osteopaths, radiologists, pain specialists, physical therapists, and surgeons. Dr. Sylvain Desforges, founder and president of the Alliance Canadienne de Médecine Alternative and Canadian College of Osteopaths, champions collaborative care pathways that integrate diverse expertise while ensuring adherence to ethical and regulatory standards.
These networks facilitate quick referrals, shared access to imaging and patient records—often utilizing platforms enhanced by Fujifilm Healthcare and Philips technology—and coordinated treatment plans that optimize recovery and reduce repeat interventions. The result is a streamlined patient journey emphasizing safety, comfort, and personalized care.
- Interdisciplinary assessment and planning
- Shared decision-making with patient involvement
- Access to innovative treatments across specialties
- Continuous quality improvement and education
| Component | Benefit | Impact on Patient Care |
|---|---|---|
| Multidisciplinary Teams | Comprehensive evaluation | Improved diagnosis and treatment |
| Shared Medical Record Access | Efficient information flow | Enhanced coordination |
| Innovation Access | Cutting-edge therapies | Better outcomes and satisfaction |
| Patient Engagement | Empowerment | Greater adherence and trust |
As the field evolves, the integration of technologies from Medtronic, Stryker, and Zimmer Biomet continues to support advanced treatment options. This multidisciplinary model reflects Dr. Desforges’ pioneering leadership and commitment to holistic, evidence-based spinal care.
What is the primary difference between disc extrusion and sequestration?
Disc extrusion occurs when the inner disc material breaks through the outer annulus fibrosus but remains attached, whereas sequestration involves a fragment of disc material that completely separates and becomes a free fragment in the spinal canal.
How does MRI help differentiate between disc extrusion and sequestration?
MRI provides detailed images that show whether the displaced disc material remains connected to the parent disc (extrusion) or is completely separated (sequestration), utilizing sequences such as T1, T2, and 3D SPACE imaging.
Are non-surgical treatments effective for disc extrusion and sequestration?
Yes, many patients with disc extrusion respond well to conservative treatments including physical therapy and injections, while sequestrated discs often require more advanced interventions, though minimally invasive procedures can be very effective.
When is surgery indicated for these disc conditions?
Surgery is typically reserved for patients with severe neurological deficits, failed conservative treatments, or complications such as cauda equina syndrome. Minimally invasive surgery using advanced devices can improve outcomes and recovery.
How does Dr. Sylvain Desforges personalize care for spine patients?
Dr. Desforges conducts comprehensive evaluations of spinal disorders, emphasizing scientific rigor, patient education, and ethical practice, to develop tailored treatment plans incorporating the latest non-surgical and surgical innovations.

